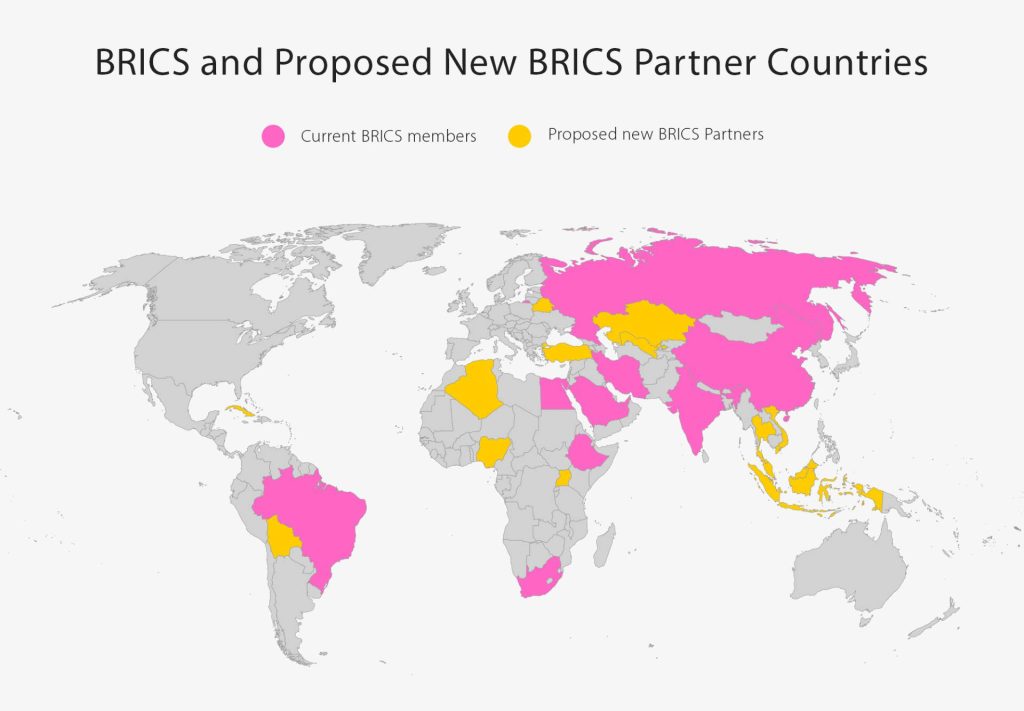
The BRICS countries have agreed to include 13 countries in the category of “Partner States” in the association. However, the entry of these countries has not yet been made official, as the newly established protocol in the procedure requires the country holding the current Chairmanship of the organisation (in this case, Russia, from 2025, Brazil) to hold consultations with the partner countries concerned.
The new bloc of countries invited to join the BRICS as “Partner States” include Algeria, Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Nigeria, Thailand, Turkiye, Uganda, Uzbekistan, and Vietnam.
According to diplomatic sources from the Brazilian delegation in Kazan, Venezuela was left off the list due to a veto by Brazil.
Brazilian Foreign Minister Mauro Vieira stated that the leading BRICS countries have reached a consensus on the ‘criteria and principles’ that will guide the bloc’s future expansion, stating that “Our discussion focused on the criteria and principles for future BRICS expansion. Currently, there are 10 member countries, but there will be more in the future. These principles and criteria have been discussed, approved, and agreed upon. Regarding the list of new members, consultations will begin soon. The Russian Chair will consult with each current member, and we will announce the countries, if not by the end of the year, then in 2025, when the responsibility will pass to the Brazilian Chairmanship of BRICS.”
This is a brief introduction to each proposed new BRICS Partner Country:
Algeria

Algeria is an oil-based economy and a member of OPEC, while its debt to GDP ratio is one of the lowest in the world at just 2%. It joined the BRICS New Development Bank and took an equity position in August this year. Algeria has the second-highest Human Development Index in continental Africa and one of the largest economies in Africa, due mostly to its large petroleum and natural gas reserves, which are the sixteenth and ninth-largest in the world. Sonatrach, the national oil company, is the largest company in Africa and a major supplier of natural gas to the European Union. The Algerian military is one of the largest in Africa, with the highest defence budget on the continent and among the highest in the world (22nd globally). Regionally, Algeria is a member of the African Union, the African Continental Free Trade Agreement, the Arab League, the OIC, OPEC, and the Arab Maghreb Union. It has a population of about 47 million, a GDP (PPP) of US$768.52 billion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at US$16,483. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 3.8%.
Belarus

Belarus is a neighbouring country to Russia, also sharing borders with Latvia, Lithuania, Poland and Ukraine. It is a major agricultural economy and a significant global producer of agricultural produce, fertilizers and agricultural machinery. It is a member of the Eurasian Economic Union, Commonwealth of Independent States and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. Belarus has a population of about 10 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$221 billion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at US$24,016. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 4%.
Bolivia

Bolivia borders fellow BRICS member Brazil to the north and is the largest land-locked country in South America. Seaport access is via Peru. Bolivia has the world’s largest lithium reserves, second largest antimony reserves, third largest iron ore reserves, sixth largest tin reserves, ninth largest lead, silver, and copper reserves, tenth largest zinc reserves, and undisclosed but productive reserves of gold and tungsten. Additionally, there are believed to be considerable reserves of uranium and nickel. Bolivia’s Lithium reserves make it a key source for future technologies, including semi and super-conductor production. Bolivia also has the second largest natural gas reserves in South America. It is a member of the Andean Community, and an associate member of Mercosur, with full incorporation pending. The Andean Community includes Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru, while Mercosur includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Bolivia has a population of about 11.50 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$125 billion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at US$10,340. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 1.6%.
Cuba

Cuba is the second largest country in the Caribbean with a predominantly agricultural economy and underdeveloped industry. The share of mining and metallurgy in the gross industrial output of the country is small – about 3% of GDP. Development of deposits and mining of nickel ores is a significant part of the Cuban economy, as the largest reserves of nickel and cobalt on the North American continent are located on the territory of the country. Since 1962, the United States has imposed harsh sanctions against it. The country has been a strategic partner of both the USSR and Russia since the Cold War and remains partially dependent on Moscow. Cuba faces problems with outdated infrastructure, while Moscow uses it as a trading partner but also as a reminder to the United States that it can station unobserved nuclear submarines very close to U.S. territory. Russian tourism to Cuba is a growing market, with Russian tourist traffic continuing to increase in the fall. Cuba has trade agreements with Mercosur and Caricom, which also includes Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Haiti, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, and Trinidad and Tobago. It is effectively the BRICS window onto the Caribbean. Cuba has a population of slightly over 10 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$255 billion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at US$22,237. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 1.7%.
Indonesia

Indonesia is the world’s largest Muslim nation, and a multi-trillion-dollar economy in its own right. It is the only G20 member state in Southeast Asia and has the largest economy in the region. Services are the economy’s largest sector and account for 43.4% of GDP, followed by industry (39.4%) and agriculture (12.8%). Indonesia is the world’s largest producer of nickel. It is also a major Asian tourism destination, and especially to Bali. Indonesia is a member of ASEAN, which also includes Brunei, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. It also has free trade agreements with Australia, China, Hong Kong, India, Japan, South Korea, and New Zealand. Indonesia has a population of about 283 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$4.66 trillion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at US$16,542. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 4%.
Kazakhstan

Kazakhstan is the largest country in Central Asia and serves as a land bridge between Europe and China. It is a major energy economy, with the second highest regional gas reserves (after Turkmenistan). Kazakhstan dominates Central Asia both economically and politically, accounting for 60% of the region’s GDP, primarily through its oil and gas industry; Major exports include crude oil and petroleum products (55.4%), refined copper and unprocessed copper alloys (5.2%), radioactive chemicals (4.6%), copper ores and concentrates (4%), and ferroalloys (2.8%). Kazakhstan is considered to be the largest uranium producer in the world, with 14% of the world’s proven reserves of this metal in the country’s subsoil. Other major exports include wheat, textiles, and livestock. Kazakhstan is a member of the Commonwealth of Independent States, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, Eurasian Economic Union, the Organization of Islamic Cooperation, and Organization of Turkic States amongst others. Kazakhstan has a population of about 20 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$693 billion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at US$34,534. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 3.9%.
Malaysia

Malaysia is centrally located in Southeast Asia, sharing land borders with Thailand and maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land borders with Brunei and Indonesia, as well as a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. One of the largest economies in ASEAN, its service sector contributes over half of total GDP, the industrial sector 37.6%, tourism about 30%, and the agricultural sector about 8.8%. Malaysia is an exporter of natural and agricultural resources, and petroleum is a major export. Malaysia remains one of the world’s largest producers of palm oil. The country has developed into a centre of Islamic banking, while knowledge-based services are also expanding. In 2023, Malaysia exported high-tech products worth over $120 billion, the second-highest in ASEAN after Singapore. Along with its membership of ASEAN, Malaysia also has free trade agreements with Australia, Chile, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Pakistan and Türkiye. Malaysia has a population of about 35 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$1.3 trillion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at US$39,000. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 5%.
Nigeria

Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa and is considered a regional powerhouse. Nigeria’s economy is the fourth-largest in Africa, and is a significant regional energy play. The country has Africa’s largest, and the worlds’ ninth largest oil reserves, however the industry is somewhat disorganised. It is also developing NPP with China and Russia. Nigeria has an abundant supply of natural resources, including underexploited minerals such as coal, bauxite, tantalite, gold, tin, iron ore, limestone, niobium, lead and zinc. Despite huge deposits of these natural resources, the mining industry in Nigeria is still in its infancy. Nigeria also has a highly developed financial services sector, with a mix of local and international banks, asset management companies, brokerage houses, insurance companies and brokers, private equity funds and investment banks. Nigeria is a founding member of the African Union the African Continental Free Trade Agreement, and a member of many other regional organizations, including the Economic Community of West African States, Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and OPEC. It has a population of about 231 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$1.45 trillion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at about US$12,000. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 3.1%.
Thailand

Thailand is another of the so-called ‘Asian Tigers’ with a significant economy, the second largest in ASEAN after Indonesia. Thailand has land borders with fellow ASEAN members Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and Malaysia, and shares maritime borders with Vietnam, Indonesia and India. It is an export manufacturing driven economy, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of GDP. These include cars, computers, electrical appliances, rice, textiles and footwear, fishery products, rubber, and jewellery. The Thai automotive industry is the largest in Southeast Asia and the 9th largest in the world, although most of its production is sold under foreign marques. Thailand also serves as an anchor economy for the neighbouring developing economies of Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia, and there is spill-over manufacturing into these countries. Thailand also has a significant tourism industry, being the most visited country in Southeast Asia. Compared to other ASEAN countries, Thailand is the largest importer of gas in weight, and it needs to continue this drive. The government has developed an Alternative Energy Development Plan which defines goals for the increase of renewable energy to almost 30,000 MW by 2037. In addition to its membership of ASEAN, Thailand also has Free Trade Agreements with Australia, Chile, China, Hong Kong, India, Japan, New Zealand, Peru and South Korea. Thailand has a population of about 66 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$1.65 trillion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at about US$23,400. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 2.6%.
Turkiye

Turkiye is an upper-middle-income country and a founding member of the OECD and G20. Services account for the majority of GDP, whereas industry accounts for more than 30%, and agriculture contributes about 7%. It has a diversified economy; main industries include automobiles, electronics, textiles, construction, steel, mining, and food processing. Turkiye ranks 8th globally in crude steel production, and 13th in motor vehicle production, ship building (by tonnage), and annual industrial robot installation. It is also developing as a gas transit hub between Russia and Europe and has a significant tourism industry. Turkiye ranks second in the world in terms of the number of international contractors in the top 250 list and is the fifth largest globally in textile exports. Turkish Airlines is one of the largest airlines in the world. Turkiye has a customs union with the European Union, and has Free Trade Agreements with Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Chile, Egypt, Faroe Islands, Georgia, Israel, Kosovo, Malaysia, Mauritius, Moldova, Montenegro, Morocco, North Macedonia, Palestine, Serbia, Singapore, South Korea, Tunisia, Venezuela, the United Kingdom and the UAE. Turkiye has a population of about 85.5 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$1.34 trillion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at about US$40,300. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 3.2%.
Uganda

Uganda is a landlocked country and requires access to the Indian Ocean via Kenyan and Tanzanian ports, an infrastructure issue that has dampened its development. However, new rail and road connectivity should improve matters in coming years. At present, it is one of the poorest countries in the world, however, Uganda has abundant energy resources, including hydropower, biomass, solar, geothermal, peat and fossil fuels, and it has crude oil reserves totaling an estimated 95 million cubic metres. The Uganda–Tanzania Crude Oil Pipeline (UTCOP), also known as the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) will be the first of its kind in East Africa and will connect Uganda’s oil-rich Hoima region with the Indian Ocean through the Tanga port in Tanzania. Otherwise, Uganda is a mainly agricultural-based economy, with products such as coffee, maize, tobacco, sugar and tea dominating. Uganda is a member of the Africa Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA). It has a population of about 50 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$145 billion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at about US$1,500. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 6.6%.
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia. It is surrounded by five countries: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan and Turkmenistan. This means that connectivity issues are important for Uzbekistan, with new railways currently under construction to better link the country to Russia, China, and seaports in Pakistan. The Uzbek economy is in a gradual transition to a market economy, with foreign trade policy being based on import substitution. Uzbekistan is a major producer and exporter of cotton. Thanks to its gigantic Soviet-era power generating capacity and vast natural gas reserves, Uzbekistan has become the largest electricity producer in Central Asia. Uzbekistan is a member of the Commonwealth of Independent States and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation and is mulling membership of the Eurasian Economic Union. It also has a General System of Preferences (GSP+) trade agreement with the European Union, which has removed tariffs on two thirds (6,200 titles) of the product lines covered by GSP. Uzbekistan also has a trade agreement with Turkiye. It has a population of about 37 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$492 billion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at about US$13,200. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 6%.
Vietnam

Vietnam is the third ‘Asian Tiger’ economy to be considered for ‘BRICS Partner’ status. A member of ASEAN, it is one of the two Marxist–Leninist states in Southeast Asia, and shares land borders with China, Laos and Cambodia. It has maritime borders with Thailand, the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia. Vietnam has been a beneficiary of the ‘China Plus One’ concept, where rising costs in China manufacturing have seen many manufacturing investors relocate or partially relocate to Vietnam, which offers similar productivity levels but at lower cost. Vietnam has also become a major exporter of agricultural products, and is the world’s largest producer of cashew nuts, the largest producer of black pepper, and the second-largest rice exporter in the world. Vietnam is also the world’s second largest exporter of coffee. Apart from its ASEAN membership, Vietnam also has Free Trade Agreements with Australia, Chile, China, Hong Kong, India, Japan, Mexico, Peru, South Korea, and the United Kingdom, as well as with the Eurasian Economic Union, which includes Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Russia. Vietnam has a population slightly over 100 million, a GDP (PPP) of about US$1.6 trillion, and a per capita GDP (PPP) estimated at about US$15,500. 2024 GDP growth is expected to reach 6.8%.
New BRICS Demographics
These potential new ‘BRICS Partners’ would change the overall BRICS dynamics in terms of global influence. In total, this expanded BRICS would account for just under 43% of global GDP, compared with the G7’s 30%. In population terms, the new BRICS, if all the proposed BRICS Partners joined, would account for about 57% of the total global population, as opposed to 10% for the G7.
In terms of simple demographics, the emergence of what may become the world’s largest multilateral organisation will start to make multiple countries think about the developing, new geopolitical dynamics and the implications. At present, it appears the West is not aware. But with another 20 countries having also applied to join BRICS, and not yet part of the overall structure – change to global geopolitics and trade flows is almost certainly arriving. The 2025 BRICS summit will be held in Brazil, when both these developments and continuing new ones will almost certainly have manifested themselves. The world is changing faster than many people realise.
Further Reading
BRICS 2024 Heads of State ‘Kazan Summit Declaration’ – Contents & Analysis

 Русский
Русский













