2025 has become a watershed in Russia-Oman relations. With Sultan Haitham bin Tariq’s historic April visit to Moscow, the first by an Omani ruler, ten agreements were sealed in trade, diplomacy, media cooperation, climate dialogue, and a mutual visa exemption programme. That visit, followed by the Russia–Oman Business Forum in Muscat on November 13, 2025, as part of a larger business mission celebrating 40 years of diplomatic ties, marks the most dynamic phase in bilateral ties since the establishment of diplomatic relations 40 years ago. That bodes well for trade and investment relations heading into 2026.
In an interview with the Muscat Daily on December 7, Aleksey Valkov, Deputy Director of the Roscongress Foundation and Director of SPIEF, highlighted the “growing depth of Russia–Oman economic ties and the emergence of new cooperation frontiers.” His assessment reflects a broader reality: both nations are positioning themselves at a moment of structural economic realignment, where logistics, energy, food security, and technology are redefining global connectivity. The establishment of the Omani–Russian Joint Intergovernmental Commission on Trade, Economic and Technical Cooperation, co-chaired by senior ministers from both nations, symbolizes the intention to move beyond traditional diplomatic warmth toward a comprehensive economic partnership centered on concrete projects, private-sector engagement, and long-term investment flows.
A Surge in Bilateral Trade

Oman-Russia trade has grown 62.3% between 2020 and 2024, reaching an estimated US$340 million by end-2024. The upward trajectory continues in 2025, powered by: increased Russian investment in Omani energy security sector, logistics and food security initiatives, Oman’s growing role as a neutral, reliable trade partner, new institutional mechanisms such as the Joint Economic Commission and expanding private-sector cooperation through OCCI, Roscongress, and the Oman-Russia Business Council.
Trade is now centered not only on hydrocarbons but also on agriculture, metals, petrochemicals, machinery, IT services, maritime logistics, and food commodities. Oman’s neutral foreign policy, robust regulatory environment, stable currency, and forward-looking economic reforms under the Oman Vision 2040 make it an ideal partner for Russian firms navigating global sanctions-era complexities. If both countries deliver on their joint ambitions and implementation plans, they can realistically push bilateral trade toward US$1 billion by 2027. Such momentum would mark a major breakthrough, signalling a new phase of strategic economic partnership. Reaching these targets won’t happen automatically – companies, businesses, and investors on both sides must show seriousness, trade pragmatism and long-term trade engagement.
For example, Russia’s first large shipments of refrigerated meat exports to Oman earlier this year showcases a deeper agricultural supply chain in the making. Oman’s meat demand is rising rapidly, driven by population growth, rising incomes, and a large Muslim population, favouring poultry, with a domestic poultry consumption projected to reach 102,000 metric tons by 2026.
This highlights a major opportunity for Russian exporters. Russian meat and poultry shipments are already on the rise, with 2024 exports hitting a record US$1.7 billion and further growth expected in 2025. Leading Russian producers are rolling out ambitious plans to strengthen their presence in Oman’s market. By 2030, Russian meat and poultry exports are projected to double to US$3.6 billion, cementing Russia’s position as a global supplier.
Oman Vision 2040: The Opening of a Strategic Gateway for Russian Companies

Oman’s Vision 2040 prioritizes: diversification beyond oil, world-class logistics hubs, private sector prioritization, value-added manufacturing and industrialization, renewable energy and hydrogen, tourism, culture, and technology and SME development and foreign investment. These align closely with Russia’s competencies in industrial engineering, energy technologies, digital transformation, agriculture, and infrastructure.
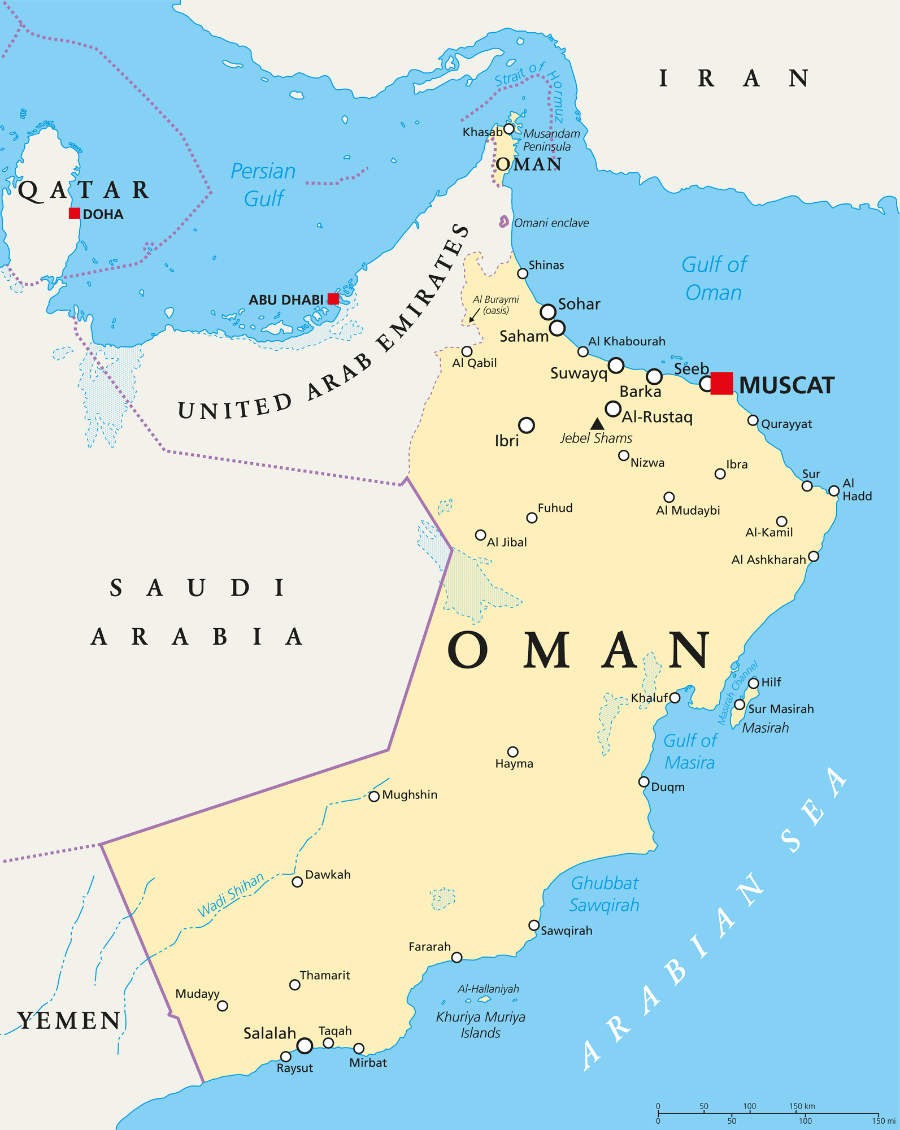
Key Opportunities for Russian Companies in Oman

- Energy & Petrochemicals
Cooperation on upstream and downstream projects, LNG technologies, petrochemical supply chains and modern oil-field services and equipment. Oman’s investment in green hydrogen positions it as an ideal site for Russian expertise in ammonia, gas-to-chemicals, and energy transition technologies.
- Logistics & the North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC)
Russia views Oman as the southern gateway of a modernized transport corridor connecting: Russia, Iran, Central Asia, India, GCC & MENA and East Africa. Deputy Prime Minister Marat Khusnullin underscored Oman’s “beneficial location for port development and access to key Middle Eastern and African markets.”
- Industrial Equipment and Engineering
Oman’s fast-growing private sector is importing new machinery, high-tech industrial equipment, and automation systems areas where Russian firms possess competitive price-to-quality advantages. Oman’s expanding industrial equipment and engineering sector powered by Vision 2040 and major infrastructure projects creates strong demand for advanced machinery and technical expertise and Russian technology transfer. Russian companies can tap this growth by supplying industrial equipment, engineering services, and technology solutions for ports, logistics hubs, and large-scale construction.
- Food Security & Agriculture
Russia, one of the world’s leading exporters of grain, poultry, and processed foods, can supply Oman’s rapidly expanding food market while developing joint agricultural investments. Oman’s agriculture market, valued at US$2.1 billion in 2025 and projected to reach US$2.86 billion by 2030, is rapidly expanding, particularly in fruits and vegetables. Russia can leverage its expertise in grains, oilseeds, and advanced agricultural machinery to support Oman’s drive toward 70% food self-sufficiency. Precision-agriculture programs open doors for Russian agri-tech solutions, including smart irrigation and crop management systems. Renewable-energy initiatives and solar-powered desalination create opportunities for Russian clean-tech and energy-efficient farming equipment. Together, these trends offer Russian companies a foothold in Oman’s modernizing, high-growth agricultural sector.
- Digitalization & AI
From cybersecurity to e-government systems, Russian tech firms can support Oman’s digital transformation agenda. The Oman AI & Digital Future Program presents a prime entry point for Russian tech firms to offer AI, cybersecurity, and digital infrastructure solutions. Russian companies can leverage this initiative to partner in Oman’s digital transformation—deploying software, smart‑city platforms, and data‑center services.
- Tourism Cooperation
With an 87% rise in Russian visitors to Oman in the first seven months of 2025 and mutual visa-free regime, tourism, hospitability management and civil aviation sectors are a rapidly expanding economic bridge. An estimated 80,000 Russian tourists are expected to have visited Oman during 2025.
Oman as Russia’s Emerging Logistics and Corporate Hub

A major shift in 2025 is the increasing number of Russian businesses relocating or registering subsidiaries in Oman, driven by UAE banks tightening compliance on Russian clients, Oman’s neutrality and lower integration with Western financial systems, simplified corporate regulations, opportunity to access Omani special economic zones (SEZs) and competitive infrastructure at Oman’s Salalah, Duqm, Sohar, and Muscat ports.
Over 30 ships formerly registered to Russian companies, including Sovcomflot and FESCO, have re-flagged to Oman this year reflecting Muscat’s rising profile as a Russian maritime and shipping base. Tighter compliance scrutiny in Dubai is driving Russian shipping toward Muscat. Oman is seizing the moment, strengthening trade and maritime ties with Russia. Oman has also become a hotspot for ship-to-ship (STS) transfers of Russian oil, particularly off its deep-water coastline. These developments underscore Oman’s emergence as the new logistical frontier in Russia’s Pivot to Asia.
Key Opportunities for Omani Companies in the Russian Market

While Russian firms benefit from Vision 2040, Omani companies also find major opportunities in Russia:
- Food Imports & Agro-Industrial Joint Ventures
Oman’s food companies can tap into Russia’s massive export capacity: wheat, barley, meat, poultry, dairy, fish and caviar and fertilizers and feedstocks. Joint ventures in agro-processing and cold-chain logistics could supply not only Oman but GCC and African markets.
- Tourism & Hospitality
Oman’s tourism operators can partner with Russian firms to attract: adventure tourists, winter holidaymakers, cultural tourists and sports and wellness travellers. Visa-free travel for Omanis (up to 30 days per visit) enhances accessibility.
- Manufacturing & Industrial Investment
Omani investors may enter Russian regions offering industrial parks, reduced taxes, special economic zones and access to Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) markets. Strategic sectors include petrochemicals, plastics, aluminium, construction materials, pharmaceuticals, and automotive components.
- Logistics and Cold Storage
As Russia strengthens transport corridors to South and East Asia, Omani investors can participate in: Russian port modernization, cold-storage networks, warehousing and re-export hubs.
- ICT and Cultural Cooperation
Media, digital platforms, education, museum exchanges, and cultural festivals are new areas of collaboration catalysed by the agreements signed in 2025.
- Security, Strategic Dialogue, and Stability
On November 11, a high-level Russian interagency delegation led by Sergey Shoygu, the Secretary of the Russian Security Council arrived in Oman, bringing together senior officials from the Interior, Foreign, Justice, and Industry and Trade Ministries. The group also included representatives from the Federal Service for Military-Technical Cooperation, Rosfinmonitoring, the Russian Guard, Rosoboronexport, Roscosmos, Rosatom, and other key state bodies, signalling Russia’s commitment to expanding multifaceted cooperation with Oman. The visit underscored the strategic depth of relations.
Discussions with Sultan Haitham and Omani officials focused on implementing agreements from the Sultan’s Moscow visit, strategic project development, regional coordination, maritime security, cybersecurity and protection of trade routes. It also included a broad spectrum of issues, spanning finance, banking, space, and peaceful nuclear energy. Enhanced security cooperation strengthens investor confidence and ensures the stability essential for large infrastructure and logistics projects.
Growing defense, military-technical cooperation between Oman and Russia opens significant opportunities for Russian defense companies. Strengthened ties could boost exports and advance strategic partnerships in the region.
- Bilateral Institutional Connectivity
Multiple new mechanisms now underpin Russia-Oman cooperation. The Omani–Russian Joint Government Committee Mandate includes identifying investment opportunities, removing trade barriers, facilitating SME partnerships, promoting research & development and coordinating bilateral exhibitions and forums. These include:
The Russia–Oman Business Forum, confirmed as a yearly fixture ensuring sustained business engagement.
Roscongress International Platform, providing an active arena for B2B networking and intergovernmental dialogue.
Oman as the 2024 SPIEF Guest Country was a milestone that dramatically expanded business contacts. These structures give the bilateral relationship a level of predictability that businesses value.
New institutional frameworks between Russia and Oman, from the Joint Government Committee to annual business forums, provide clear channels for investment and trade. Platforms such as Roscongress and Oman’s 2024 SPIEF participation strengthen B2B networking and intergovernmental dialogue. Together, these mechanisms create predictability and confidence, making it easier for businesses to expand and engage in the bilateral market.
Russia and Oman As Natural Partners in a Shifting Global Economy

The global economy is undergoing a profound rebalancing. Amid supply chain reconfiguration, de-dollarization debates, and the rise of multipolar trade corridors, Russia and Oman find themselves strategically aligned.
Complementary Strengths
Russia Oman
Vast energy resources Strategic geography at Indian Ocean crossroads
Massive agricultural outputs Advanced ports and SEZ infrastructure
Engineering and industrial expertise Investor-friendly, Vision 2040 reforms
Major Arctic & Eurasian assets Neutrality and stable political climate
Advanced military & security capabilities Diversification in logistics, tourism, industry
Renewable and nuclear energy resources Renewable and nuclear energy ambitions
Oman’s consumer packaged goods (CPG) market is estimated to reach US$20.7 billion in size by 2033. The market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% from 2025 to 2033. Steady growth reflects rising consumer demand, urbanization, and increasing disposable incomes. Opportunities exist for Russian exporters to enter or expand in the market. Together, these assets form a powerful partnership for competing in Gulf, Asian, and African markets.
Deepening Sectoral Integration and Regional Reach

- Logistics and Infrastructure
Enhancing Oman’s role in the extended INSTC corridor, including potential onward outreach into Afghanistan and East Africa. Russian participation in Omani port development and expanded maritime links to East Africa. - Energy & Transition Industries
Oil & gas exploration joint ventures, hydrogen and renewables and petrochemical projects.
- Food Security
Long-term agricultural supply agreements and joint production facilities
- Digital Economy
Tech parks, cyber cooperation and e-commerce corridors. Bilateral currency settlement is essential for reducing costs, stabilizing trade flows, and insulating transactions from external pressure.
- Cultural and People-to-People Exchange
Rising tourism flows, university partnerships and media collaborations
These dimensions shape a partnership not just of governments, but of societies and private enterprises.
Summary: A Partnership Poised for Global Relevance
As Russia and Oman mark their 40th anniversary of diplomatic relations, the bilateral relationship is transitioning from cordial historical ties to a robust, strategically comprehensive economic partnership. The opportunities for businesses on both sides are vast. Russian companies find in Oman a gateway to the Gulf, Africa, and South Asia supported by Vision 2040, world-class ports, and a welcoming regulatory framework. Omani companies gain access to Russia’s immense market, resource wealth, industrial capacity, and the wider Eurasian Economic Union.
The narrative emerging from 2024-2025 from Sultan Haitham’s state visit to Moscow, to the SPIEF partnership, to the Muscat business forum, the new Joint Economic Commission, and heightened security dialogue signals one reality: Russia and Oman are constructing a new economic corridor grounded in trust, opportunity, and shared strategic vision. In an era defined by shifting supply chains and new geopolitical alignments, this partnership stands as a model of constructive international cooperation, one that promises prosperity for businesses, stability for governments, and opportunity for the peoples of both nations.
This article was written by MD Rana, an independent researcher, author, freelance columnist, and international affairs analyst. He may be reached via info@russiaspivottoasia.com
Further Reading

 Русский
Русский














