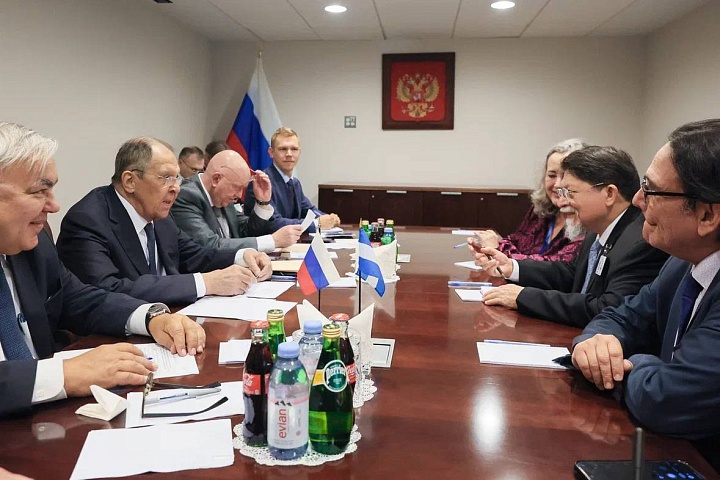
The Russian Foreign Minister, Sergey Lavrov has met with Denis Moncada, the Foreign Minister of Nicaragua on the sidelines of the 80th Session of the United Nations General Assembly in New York.
They praised the dynamic of the mutual political dialogue and the allied nature of their interaction in the international arena to protect the principles of international law, national sovereignty and non-interference in the internal affairs of states.
They also noted their readiness to further increase the entire range of bilateral relations in their strategic partnership.

Nicaragua plays a significant role in Central America’s economic landscape, and is a member of the Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) provides preferential access to the U.S. market, benefiting exports like textiles, coffee, and beef. As a member of the Central American Economic Integration System (SIECA), Nicaragua enjoys free movement of goods, services, and capital within the region, fostering greater economic cooperation. The Nicaragua-Mexico Free Trade Agreement facilitates access to the Mexican market, particularly for agricultural products and textiles. Through the EU-Central America Association of Countries FTA, Nicaragua benefits from tariff reductions and expanded access to European markets, especially in agriculture and manufacturing. Nicaragua is also part of ALADI, which promotes regional economic integration in Latin America, and the China-Nicaragua Free Trade Agreement. Nicaragua is politically supportive of Russia.
Agriculture remains a fundamental pillar of the country’s economy, with a substantial portion of the population employed in this sector. Major agricultural exports include high-quality Arabica coffee, beef, sugar, peanuts, shrimp and lobster, tobacco, cigars, and textiles, which are primarily exported to markets in the United States, Mexico, and China. The manufacturing sector, which constitutes approximately 37% of Nicaragua’s GDP, is diverse and expanding. Key industries within manufacturing include textiles and apparel, food processing, chemicals, machinery and metal products, petroleum refining and distribution, beverages, footwear, wood products, and electric wire harness manufacturing. The textile sector, in particular, benefits from preferential access to international markets through trade agreements, contributing significantly to Nicaragua’s export revenues. The services sector, with a strong emphasis on trade, transportation, and telecommunications, plays a critical role in reinforcing Nicaragua’s export-oriented economy. Trade activities represent 90% of the country’s economic output, making Nicaragua one of the most trade-dependent nations in the region. In addition, the mining sector, which has a long history in Nicaragua, continues to expand, especially in the Northern and Southern Caribbean Coast Autonomous Regions, where both metallic and non-metallic mining activities are gaining momentum.
With a population of approximately 6.4 million, Nicaragua has a GDP (PPP) of US$57 billion and a GDP per capita (PPP) of US$8,500. The expected 2025 GDP growth rate is 4%, indicating positive economic trends, driven by its key agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
Russia’s bilateral trade with Nicaragua is about US$120 million, with the bulk of this being Russian exports of nitrogenous fertilizers and vaccines, while Nicaragua exports primarily ground nuts and coffee to Russia.
Nicaragua formally recognised the new Russian regions of the Donetsk People’s Republic, the Lugansk People’s Republic, the Zaporozhye and Kherson regions, and the City of Sevastopol in late September and stated its intention to cooperate with them.
Previously, Nicaragua’s special representative for developing relations with Russia, Laureano Ortega Murillo, stated that Nicaragua plans to expand its ATM network to accept cards from Russia’s national Mir payment system, and may also begin issuing Mir cards in the future. These would dispense both Nicaraguan Cordoba and US dollar bills.
Other recent developments have included the surveying of Caribbean waters by a Russian maritime research vessel, with data on marine stocks being shared with Nicaragua and Venezuela amongst other regional nations. That can be expected to result in future fishing and port development collaborations.
Further Reading

 Русский
Русский














