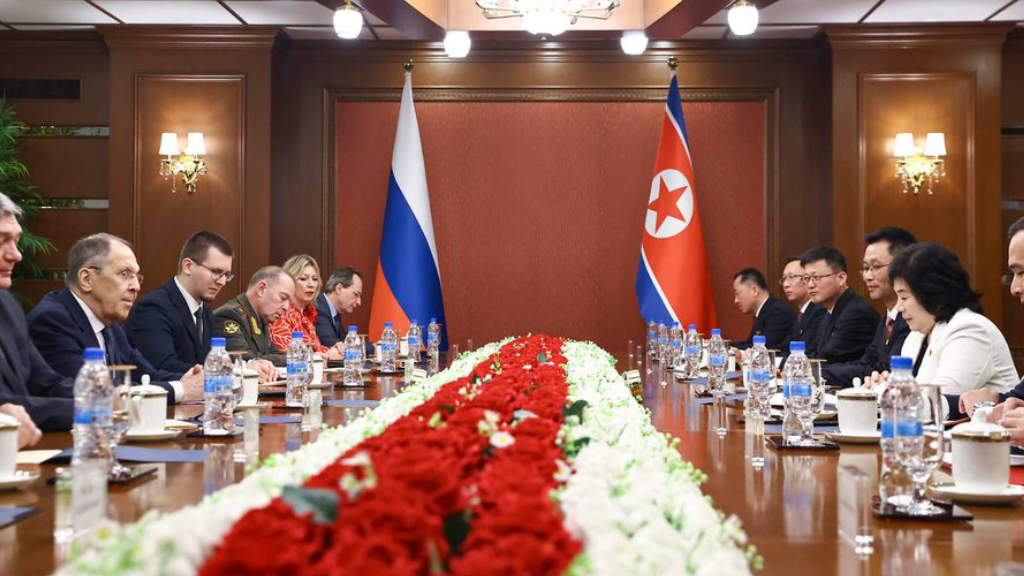
Russia’s Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov and Choe Son Hui, the Foreign Minister of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, have been holding three-day talks as part of the second round of the strategic dialogue between Russia and North Korea in the new North Korean city of Wonsan on July 11. Kim Jong Un presided over the ribbon-cutting ceremony at the Wonsan resort on June 24. It has been described as ‘world class,’ with Kim keen to have inbound tourist arrivals from friendly countries to boost North Korea’s foreign exchange revenues.
Lavrov said Russian authorities would facilitate an increase in tourist flows from Russia to the North Korean resort by creating the conditions necessary, such as resolving air travel arrangements. Direct Pyongyang-Moscow and Pyongyang-Khabarovsk rail services have already resumed.
Russia and North Korea signed a Strategic Partnership Agreement on 18 June 2024 during a visit by Russian President Vladimir Putin to North Korea. The treaty, which includes a mutual defense clause, introduces a deeper level of bilateral cooperation between the two countries, including in trade and investment.
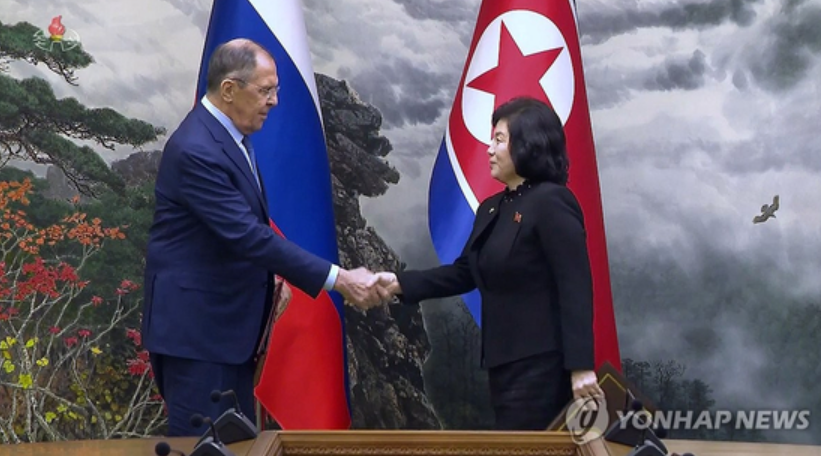

Lavrov’s visit comes less than a month after Pyongyang agreed to send an additional 6,000 military and civil engineers to Russia’s Kursk region to assist with reconstruction. Russia is currently in the process of developing a large border area between East and West Ukraine to effectively partition the country between its Western-backed West and the Russian-supporting East. North Korean engineers are presumably carrying out part of this work.
Elsewhere, bilateral connectivity is being upgraded, with improvements to road and rail border crossings being made, including new bridges built across the Tumen River border between the two countries.
Russia is also expanding its agricultural exports to North Korea and will probably follow this through with exports of fertilizers. North Korea is also rich in rare earths and other natural resources estimated at being worth up to US$10 trillion. However, these will require investment to extract and utilize, with both China and Russia evaluating the extraction cost and returns. Nonetheless, future Russian investment in mining North Korea’s minerals can be expected to materialize at some point.
The volume of bilateral trade is difficult to estimate, as most of it is not reflected in open sources of information. However, on the sidelines of the AEI roundtable “North Korea: Closed Market – Open Opportunities,” held on June 10 in Moscow, the chairman of the logistics committee of the Association of Exporters and Importers (AIE), Yevgeny Nikiforov, said that trade turnover last year reached $34 million, a record figure since Soviet times. According to Nikiforov, the growth is mainly due to exports from Russia. “These are mainly food products – flour, soybeans, oil, and grains. The second largest block is, of course, hydrocarbons,” Nikiforov said.
In reality it will amount to billions of dollars, and according to the head of Ukraines military intelligence Kirill Budanov, North Korea sends to Russia an estimated 40% of its ammunition requirements in the Ukraine conflict. It also sent thousands of troops to engage in Ukraine in addition to the engineers being sent to Kursk. Russia, in return, will have reciprocated, probably in other military hardware and software in addition to financial capital. It is highly likely that Russia’s overall trade with North Korea has overtaken its trade with South Korea, estimated to be about US$10 billion in 2024.
Lavrov and Choe will also have discussed South Korea, where the new president, Lee Jae-myung, is known to be more favorable towards improving ties with North Korea than his predecessor.
Further Reading

 Русский
Русский