
The Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov has arrived in the Republic of Congo, where he will hold meetings with Sassou Nguessou, the President along with other leaders. Discussions are being held in Oyo city.
This year marks the 60th anniversary since the establishment of diplomatic relations between Russia and the Republic of Congo, while Nguessou attended last years Russia-Africa Summit in St.Petersburg. He met with Russian President Vladimir Putin last July, who noted that “leading Russian companies, including Lukoil, Yandex, and Rosatom, are working effectively in Congo.”
Discussions are likely to focus on further promotion of trade and economic ties. According to data provided by Putin at the negotiations in July 2023, trade turnover between Russia and the Republic of Congo soared by 85% in January-April 2023. Overall bilateral trade however is relatively small at about US$250 million. Russia exports wheat and petroleum products, while the Congo exports mainly fruits.
The Congolese energy sector will be high on the agenda, as Republic of Congo proven reserves of crude oil are estimated at 1.6 billion barrels, while earlier this year, Congo announced plans to start exporting liquefied natural gas, producing the first batch at the Marine 12 project of the joint venture between Italy’s Eni and Russia’s Lukoil. The reserves of natural and associated gas in the country were estimated at 90.6 million cubic meters.
Military-technical cooperation will also be among the topics of negotiations between the head of Russian diplomacy in the Congo. In 2019, a contract was signed to send Russian military specialists to this African state. Also, at that time, negotiations were held on the supply of new Russian military equipment to the Republic of Congo.
As noted at the Russian Embassy in Brazzaville, an important area of bilateral relations is also humanitarian cooperation, “interaction in the training of Congolese personnel in Russian universities is intensively developing.” In the 2023-2024 academic year, the number of government scholarships for the Republic of Congo was increased to 250. The Russian Center for Science and Culture operates in Brazzaville.
The Republic of Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, West Congo, the Congo Republic, ROC, or simply either Congo or the Congo, is located on the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo River. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to the northwest by Cameroon, to the northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda, and to the southwest by the Atlantic Ocean.
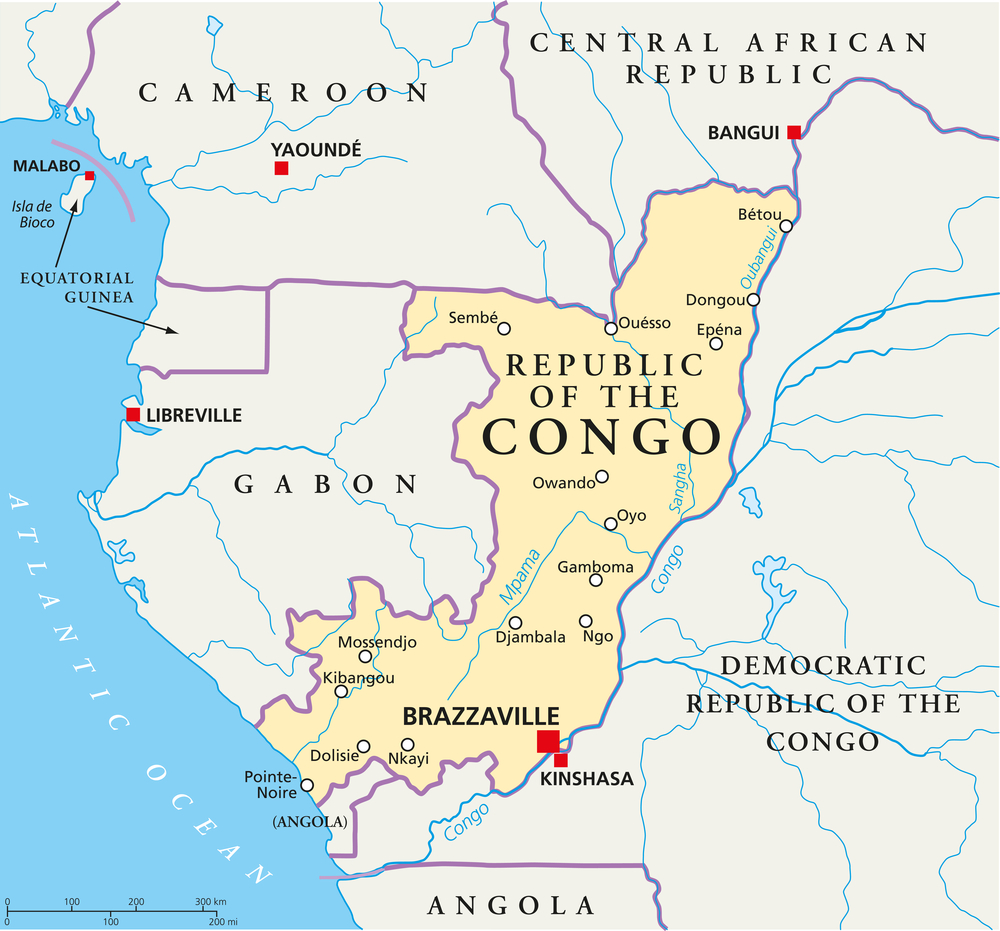
The Republic of the Congo is a member of the African Union, the United Nations, La Francophonie, the Economic Community of Central African States, and the Non-Aligned Movement. It has become the 4th-largest oil producer in the Gulf of Guinea, providing the country with a degree of prosperity. Its economy is largely dependent on the oil sector.
Like several countries in Africa, The Congo was a French colony. Russian assistance is now preferred, with ties dating back to the Soviet era.
The economy is a mixture of village agriculture and handicrafts, an industrial sector based mainly on petroleum, and related support services. Petroleum extraction has supplanted forestry as the mainstay of the economy, accounting for about 65% of the GDP, 85% of government revenue, and 92% of exports. The country has relatively untapped mineral wealth including base metal, gold, iron, and phosphate deposits along with diamonds. It has a GDP (PPP) of about US$28 billion and a total population of about 6.5 million.
Further Reading
Russia-Africa 2024 Trade & Development
Russia’s trade and investments in Africa are extensively discussed in our 2024 Russia’s Pivot To Asia guide. This is a complimentary download and can be accessed in English here and Russian here.

 Русский
Русский













