The Russian President, Vladimir Putin, used his trip to Alaska to meet US President Trump to additionally visit the Russian Far East regions of Magadan and Chukotka. (We commented on the Putin/Trump summit exclusively on our X account here). These regions are the farthest east of the entire Russian landmass, while overall the Russian Far East economy has been booming and is now responsible for attracting about 30% of Russia’s total inbound foreign investment, mainly on infrastructure investment capital from China.
Magadan

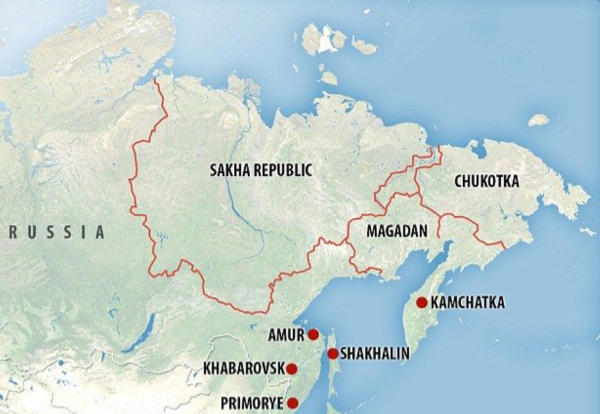
Putin stopped off at Magadan on his way to Alaska, being the capital city of the Magadan Oblast in the Far East. The city has a population of about 100,000, while Magadan port is the second largest seaport in the Russian Northeast.
Putin met with regional Governor Sergei Nosov and visited a fish oil processing plant, a sports complex and a cultural centre, and also laid flowers at a memorial to the World War II-era Alaska-Siberia air route, a symbol of Soviet-American wartime cooperation. The local economy is based on some gold mining and fisheries, with the fish oil plant being operated by Omega-Sea – a unique fish oil processing and refining plant that produces encapsulated high-concentration Omega-3 products. This is Russia’s first facility manufacturing re-esterified triglyceride (rTG), utilising premium sardines and herring sourced from the Sea of Okhotsk.
There is currently no operating railway in Magadan. However, Russian Railways are considering the possibility of building a railway from the Nizhny Bestyakh of the Amur-Yakutsk railway to Magadan by 2035, which will contribute to the development of an area with huge mineral deposits. Magadan is also the home of the Magadan/Sokol Flight Information Region (FIR) and Magadan Oceanic FIR, which controls the northeastern part of Russia and its Arctic airspace. Westbound transpacific flights from North America to Asia use these FIRs.
Chukotka

Following his visit to the United States, Vladimir Putin arrived in Anadyr, the capital of Chukotka Oblast, where he held a working meeting with the region’s Governor, Vladislav Kuznetsov. Chukotka is the easternmost federal subject of Russia and has a maritime border on the Bering Strait with Alaska to the east. Anadyr is the largest town and the capital and the easternmost settlement to have town status in Russia. It is the closest point from Russia to the United States, just 88.5 kilometres distant, and is the only part of Russia in the Western Hemisphere. The population is about 55,000.
Chukotka has large reserves of oil, natural gas, coal, gold, and tungsten, which are slowly being mined, but much of the rural population survives on subsistence reindeer herding, whale hunting, and fishing. The urban population is employed in mining, administration, construction, cultural work, education, medicine, and other occupations.
Kuznetsov reported that Chukotka’s economic performance has been robust. In the Russian Far East, it ranks second in terms of industrial output and fourth in terms of fixed capital investment, with the number of new SMEs growing. In agriculture, hothouses have been modernised, which will make it possible to produce 30% more vegetables compared to 2023. Having built three new poultry farms, the region now completely meets its demand in eggs.
Extraction of mineral resources has been increasing, making Chukotka the fourth largest mineral-producing region in the Far Eastern Federal District, while social indicators are among the best in Russia. Chukotka ranks sixth in the annual ranking of Russian regions in terms of investment appeal. Chukotka has three preferential special economic zones.
Mineral production is growing, making Chukotka the fourth largest in the Far Eastern Federal District, and its social indicators are among the best in Russia. Chukotka ranks sixth in the annual rating of Russian regions in terms of investment attractiveness. This is a unique region, as only here there are three preferential regimes at once: the Chukotka Advanced Development Territory (ADT), the Free Port of Vladivostok (FPV) and the Arctic Zone of the Russian Federation (AZRF). Depending on the type of activity and the favorable conditions offered by the state, an investor can choose the most suitable option for him/her.
The Chukotka Autonomous District is home to one of the world’s richest mining provinces, the Baim copper porphyry area, which includes 13 deposits with a resource potential of 23 million tons of copper, as well as gold, molybdenum and silver resources. In 2018, at the Eastern Economic Forum, Vladimir Putin gave the go-ahead for the development of the Baim ore zone. The Baimsky mining and processing plant (MPP) is Russia’s first copper ore mining facility that will utilize drone technology and the Internet of Things. Rosatom is building four modernized floating power units (FPU) to supply power to the Baimsky mining combine. The first two are planned to be connected to the grid by 2028, another one to be put into operation by 2029, and a fourth, standby replacement power unit to be connected to the grid by 2031. Providing energy to one of the world’s largest deposits will increase copper production in Russia by 25%. In addition, a major project to develop the Pyrkakai Stockworks deposit – the Pyrkakai Mining and Metallurgical Combine – will make Russia an exporter of tin. Construction of the combine is scheduled to begin in 2025, and its launch with a design capacity of 6,000 tons of tin per year is scheduled for 2030.
Kuznetsov also reported that master plans have been developed for the main towns of Chukotka’s Anadyr region, with Egvekinot, Pevek and Bilibino, are home to 82% of the population. There are plans to build numerous social infrastructure facilities, including a sports centre, swimming pool, creative industries centre, local theatre and opera house, as well as medical and water-treatment facilities.
Kuznetsov also recalled the presidential decision to order hovercraft for Chukotka to improve transport, stating that these are already operational. Work is also underway to expand accessibility in logistics since the region lacks permanent automobile roads and has no railways. The main transport is aviation. Four new helicopters have been added in the past two years, with two more to arrive in September.
The Governor also reported on the way the region has been working on communications issues. It is working together with the Ministry of Digital Development to create a cable internet network. A fibre-optic communications line in the Anadyr agglomeration has been laid under the sea with plans to connect it to Yakutia.
Further Reading
Russia Increases Far East State Development PPP Budgets

 Русский
Русский













